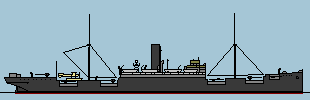
Wolf II 1917
Contruction Data
| Laid down: |
Flensburger Schiffbaugesellschaft, 1913 |
| Launched: |
08.03.1913 |
| Commissioned: |
16.05.1916 (as auxiliary cruiser) |
| Fate: |
scrapped April 1931 |
| Costs: |
|
Technical Data
| Size: |
11200 t |
| Length: |
135,0 m |
| Beam: |
17,12 m |
| Draft: |
7,8 m |
| Armament: |
5 -7 x 15 cm; 3 x 5,2 cm; 2-4 x 50 cm torpedo tubes;
465 mines, float plane Friedrichshafen FF 33E
|
| Performance: |
2800 shp, 10,5 kn |
History
The former transport ship Wachtfels
was the prototype for the auxiliary cruisers used in World War II. For the first time, an auxiliary cruiser was equipped with a float plane for reconnaissance duties - the so called Wölfchen
(little Wolf), which was used intensively during the operations of the ship. Between November 1916 and February 1918, the Wolf operated in the longest mission of an auxiliary cruiser in World War I. In its 16 month voyage, the ships was able to sink or capture 13 allied ships while operating in all oceans of the world.
After its return, the ship was used as an auxiliary vessel in the Baltic Sea. In April 11919 it was delivered to France where it sailed as Antinous
until 1931 when it was scrapped.
|
|